The main bulk of CO2 emissions produced throughout the lifecycle of our construction equipment is centered on product operation, during which approximately 80 to 90% of emissions are produced. We have acknowledged this fact, and are working to reduce these operational emissions through three different initiatives: “DANTOTSU Products”, “DANTOTSU Service”, and “DANTOTSU Solutions”.

We provide products with excellent fuel efficiency and electrification technologies that contribute to reducing CO2 emissions from our machines.
As of April 2025, eight models of our battery-powered and cable-powered electric hydraulic excavators have been certified under the “GX Construction Machinery Certification System”, which was launched by Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism to promote decarbonization at construction sites through the adoption of electric construction equipment.
In addition, as of April 2025, 25 models of construction equipments with excellent fuel efficiency —including the bulldozer D71PX-24, the hydraulic excavator PC200i-12, and the wheel loader WA150-8—have been certified as “Construction Machines Fulfilling Fuel Economy Standards” by the Ministry, recognizing their outstanding fuel performance.
The Komatsu Tracking System “Komtrax” is a system developed by Komatsu that automatically gathers the operational information/health information of our construction vehicles that operate all over the world, making it possible to then monitor/manage/analyze the vehicles remotely. Information with regards to operation times, fuel consumption, and other such relevant data is communicated to our customers via the internet, which is then analyzed to create opportunities for improvement. This enhanced operational efficiency helps to reduce fuel consumption, which results in a reduction in overall CO2 emissions.
In 2013, Komatsu introduced the world’s first automatic blade control ICT bulldozer, D61PXi-23, to the North American, European, and Japanese markets. Following this, in 2014, Komatsu developed and released a hydraulic excavator with semiautomatic control functions (PC210LCi-10 for North America and Europe, and PC200i-10 for Japan). Preliminary calculations based on in-house testing were promising, with construction data for ICT hydraulic excavators showing that fore-slope shaping work using the PC200i-10 resulted in an approximate reduction of 30% in fuel consumption. In addition, the same testing showed that ICT bulldozers (like the D61DXi-23) used in land preparation work resulted in an approximate reduction of 25% in fuel consumption. Our testing with hydraulic excavators also showcased a significant decrease in CO2 emissions.
To consolidate our efforts in this sector, Komatsu is implementing “Smart Construction”, a system that uses ICT-type construction machines alongside drones and 3D scanners to take real-time topography measurements. This initiative helps showcase the efficiency of our machines by recording progress in construction sites and other relevant performance indicators.
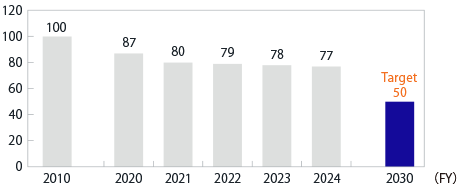
Komatsu has set the target of reducing the CO2 emissions from the operation of products (such as construction, mine, and forestry equipment) by 50% by FY2030 (compared to FY2010).
To evaluate progress toward this goal, we compared the performance of the current year’s products to the products of the base year (FY2010) and estimated CO2 reductions through the improvement of fuel consumption and work efficiency. The products of FY2024 achieved a CO2 reduction of 23%, compared to the base year.
CO2 emission index for product operationsIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
This model is a next-generation version of the electric micro excavator "PC01E-1" (hereinafter referred to as the "previous model"), which was introduced to the domestic market as a rental unit in March 2022. Like the PC05E-1, which was launched in October 2023, this model is equipped with a removable portable battery "Honda Mobile Power Pack e:" (*1) and an electric power unit "eGX" (*2) as its power source.
Since the introduction of the previous model, it has been well received for its quiet operation, zero emissions, and the convenience of requiring only battery replacement instead of fuel refills. Additionally, it offers comparable excavation performance to the engine-powered model "PC01-1". For this model change, we specifically incorporated requests for slimming down the rear section. The number of batteries has been reduced from two to one and positioned in the center of the vehicle (midship layout). As a result, the overall length is about 20 cm more compact than the previous model, while achieving greater stability than the engine-powered "PC01-1", further enhancing usability. This model has already been certified under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism's GX Construction Machinery Certification System (*3), making it the 8th certified model from Komatsu. Komatsu will continue to work on developing products and solutions that meet customers' needs for reducing environmental impact.


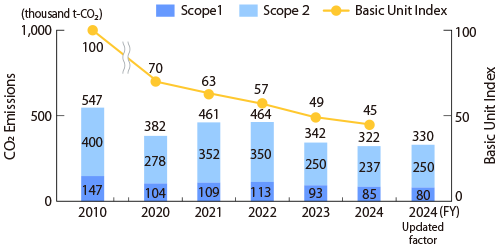
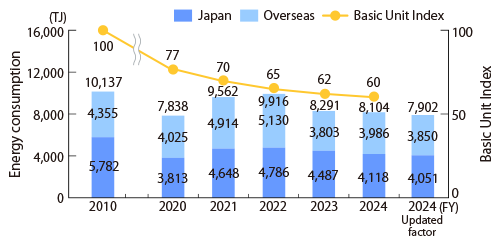
As part of our efforts to address climate change, Komatsu promotes activities to reduce CO2 emissions per unit of internal manufacturing value, using this as a key indicator, for all energy used in research, development, and production at our global locations, including electricity, gas, and oil.
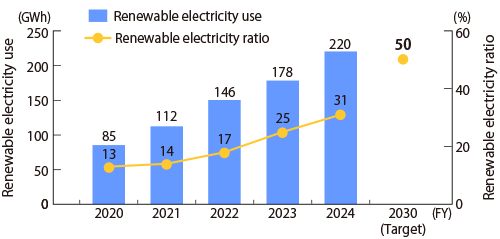
In FY2024, energy-saving improvements focused on high-load plants in Japan and overseas (such as those for casting, forging, heat treatment, and machining), the expansion of solar and biomass power facilities, and increased purchases of green electricity overseas have significantly reduced our CO2 emissions per unit. Additionally, the proportion of renewable energy used in our electricity increased to 31%.
Since FY2021, Komatsu has set an internal carbon pricing (ICP)* of USD 300 per ton of CO2 and has applied it to decision-making for energy-saving and renewable energy investments related to Scope 1 and Scope 2, thereby promoting environmental improvement investments.
| Item | FY2023 | FY2024 | Target of FY2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 emissions basic unit (compared to FY2010) | 49 | 45 | 50 |
| The rate of renewable energy use | 25% | 31% | 50% |
Japan
Overseas
Energy related CO2 emissionsIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
The amount and ratio of renewable electricityIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
Energy consumption
Independent Practitioner's Assurance
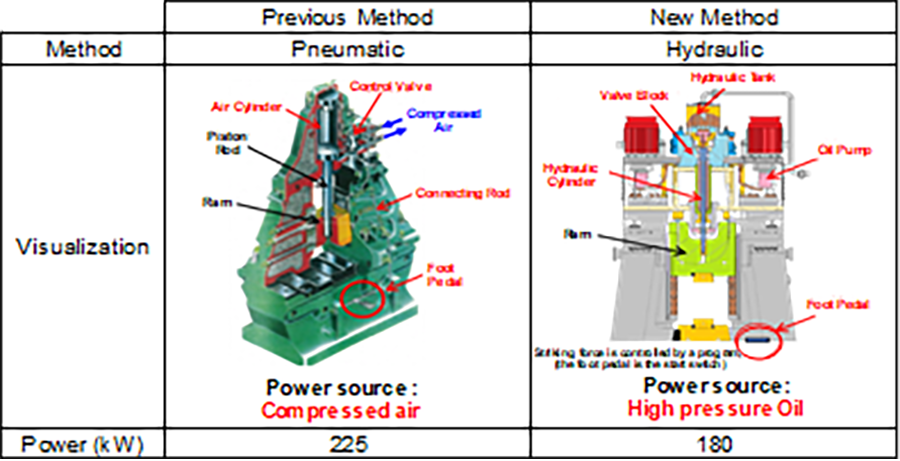
PT Komatsu Undercarriage Indonesia (KUI), which manufactures and sells crawler components and parts for construction and mining equipment, is Komatsu’s third-largest CO2-emitting plant. The highest emissions come from the forging plant, making up 85% of KUI's total emissions, and 23% of the forging plant's emissions come from air compressor use.
Forging is an energy-intensive process, especially when using conventional pneumatic hammers that require large amounts of compressed air and electricity. These systems are less efficient because of significant energy loss during air compression and distribution.
Since FY2018, KUI has been working to reduce CO2 emissions, especially in the forging process, by replacing pneumatic (air drop) forging hammers with energy-efficient hydraulic forging hammers. Hydraulic hammers offer higher operational efficiency and significantly reduce unnecessary energy consumption. KUI initiated a project to replace several pneumatic forging hammers with hydraulic forging hammers.
Through this improvement:
Overall, the hammer conversion plan is expected to reduce KUI’s forging plant emissions by 5 kT CO2 by FY2029, contributing significantly to KUI's carbon neutrality targets. By continuously upgrading to more efficient equipment, KUI demonstrates a strong commitment to environmental sustainability while maintaining production performance.

(Basic unit of CO2 emissions per cargo weight)
Komatsu is promoting modal shift to use coastal vessels and railways in domestic transportation while enhancing transportation efficiency by improving the loading ratio. Additionally, to shorten transportation distances to ports for export products, we actively use Kanazawa and Hitachinaka ports, which are located near our manufacturing sites.
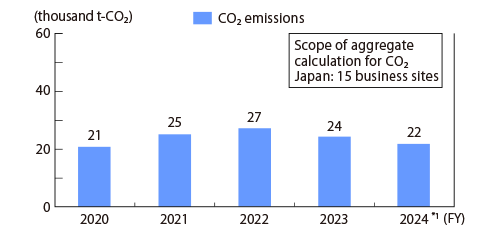
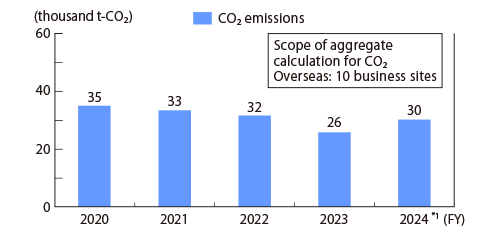
In FY2024, modal shift improvements progressed particularly well in Japan, and CO2 emissions from domestic transportation totaled 21.7 thousand t-CO2. As a result, the Intensity per ton-kilometer was reduced by 1 point compared to the previous year. On the other hand, in overseas operations, a decline in production volume led to a total of 30.1 thousand t-CO2 emissions from transportation, with the Intensity per cargo weight deteriorating by 1 point from the previous year.
Komatsu will continue working to improve transport efficiency both domestically and globally, and remain committed to reducing CO2 emissions associated with logistics.
CO2 emissions in transport Japan
Independent Practitioner's Assurance
CO2 emissions in transport Overseas
Independent Practitioner's Assurance
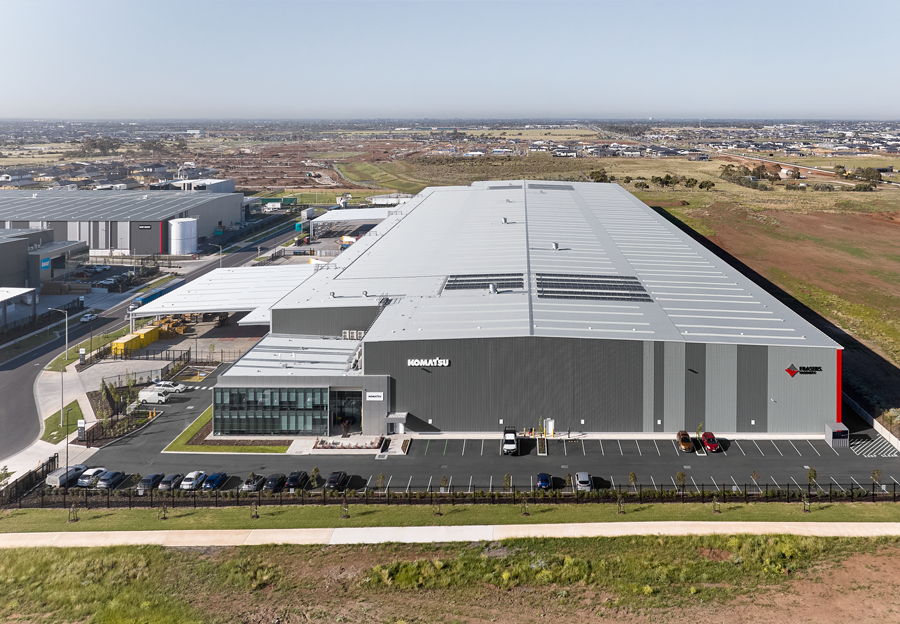
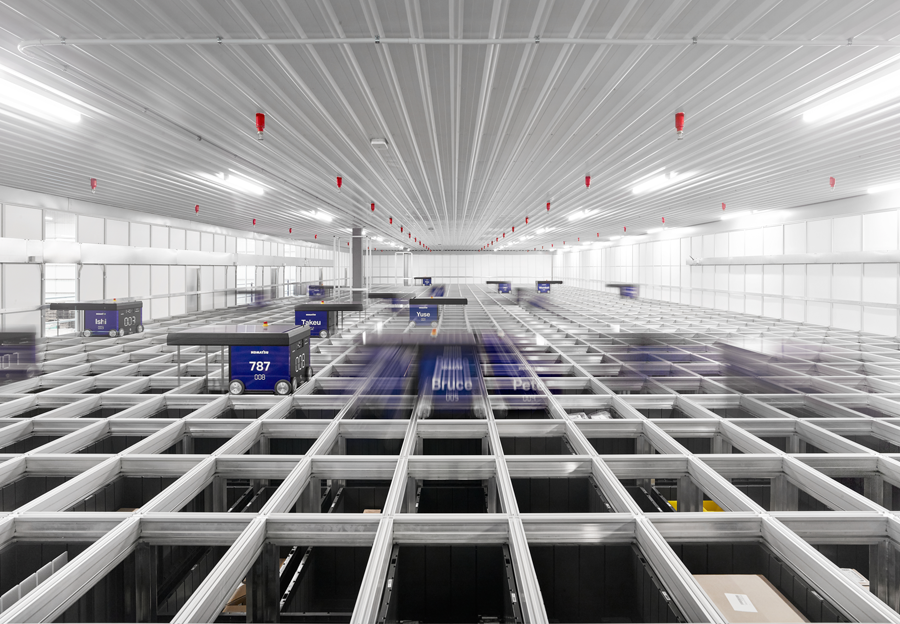
AutoStore is the latest initiative by Komatsu Australia Pty.Ltd (KAL) and has been implemented at the Melbourne Fulfillment Center (FC) in Victoria, Australia. This technology automates the entire distribution process by using robots to automatically store and retrieve parts.
By having robots deliver items directly to the picking stations instead of pickers spending considerable time searching for products and walking, the overall picking time is significantly reduced.
Each robot is highly efficient, consuming only 0.1 kilowatts (kW) of power per hour. Six robots consume about the same amount of energy as one toaster.
* The six robots have been named Wombat, Bruce, Pete, Takeu, Yuse, and Ishi. For example, if this solution operates 12 hours per week over 52 weeks annually, the total annual electricity consumption would be 3,744 kilowatt-hours (kWh), which corresponds to less than 10 kWh per day.
This compact and space-saving system has further improved efficiency, enabling the consolidation of all construction spare parts storage into a single facility.

