Komatsu complies with national and local laws and regulations and ensures that it periodically reports and maintains measurement results.
In FY2024, there were three minor violations of environmental regulations in Japan. No fines were imposed, and all issues have been resolved. There were no environmental violations at our overseas sites.
Komatsu has established guidelines for testing soil and groundwater, inspects any business unit that is scheduled to be sold, closed, or removed pursuant to laws and regulations, and takes purification measures upon confirmation by local authorities if contamination is discovered.
We voluntarily investigate business units in operation in order to test for contamination stemming from VOCs in cleaning solvents, etc. used in the past.
We have been surveying soil and groundwater for VOC contamination at domestic business units since 2005, and have implemented countermeasures at any sites that have been found to be contaminated. We use methods that facilitate the cleaning process in the shortest period of time possible.
We will continue to thoroughly clean-up and regularly monitor groundwater at site boundaries to ensure that there is no outflow of groundwater that has exceeded the standard outside the premises.
At our sites in Japan, PCB-containing waste—such as transformers and fluorescent lamp ballasts—is properly stored and disposed of in accordance with the “Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes” and the “Waste Management and Public Cleansing Law.”
While Komatsu completed the disposal of high-concentration PCB waste by the legal deadline (end of March 2023), some high-concentration PCB-containing fluorescent lamp ballasts were discovered in April 2025 in older buildings at a few sites. These were promptly reported to the relevant authorities, and based on their guidance, we plan to complete the disposal within this fiscal year. We have also shared this case internally to prevent recurrence and will appropriately address any similar cases, should they arise.
Regarding low-concentration PCB waste, we will continue to dispose of it in a planned and systematic manner.
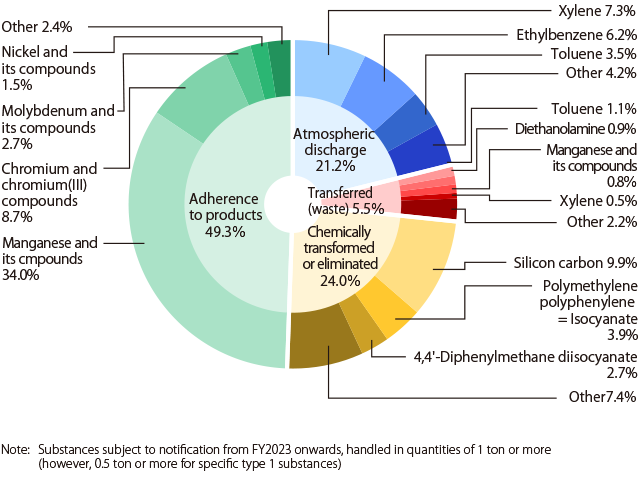
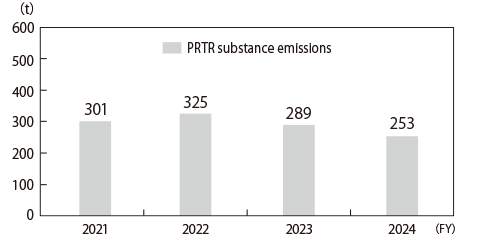
In FY2024, the number of PRTR* substances with a handling volume of 1 ton or more (0.5 tons or more for Class 1 Designated Chemical Substances) increased 4 from the previous fiscal year, reaching a total of 29 substances. This increase is due to the addition of new substances subject to PRTR following the revision of the PRTR law.
The three substances, xylene, ethyl benzene, and toluene, account for approximately 80% of the emissions from Komatsu and Komatsu Group production sites, with most of these emissions being released into the atmosphere.
In FY2024, each business site has been making improvements by switching to paints and thinners with lower PRTR Class 1 content, resulting in a reduction in the handling volume.
In FY2025, we will continue to switch to sub-materials with lower PRTR Class 1 content, improve coating efficiency, reduce coating film thickness, and recycle paint thinner.
Komatsu Group Manufacturing Facilities in JapanIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
Komatsu Group Manufacturing Facilities in JapanIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
NOTE: Substances handled in quantities 1 ton or more (0.5 tons or more for Class 1 specified)
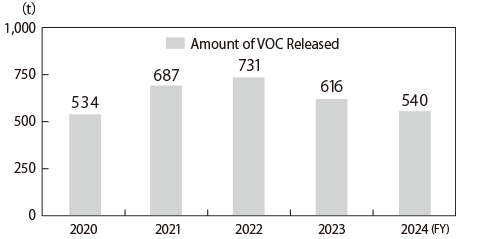
The majority of VOC emissions are from VOCs contained in paint and thinner, such as xylene and ethyl benzene.
In FY2024, VOC emissions decreased by approximately 12% compared to FY2023. We will continue our efforts to reduce VOC emissions in the future.
Komatsu Group Manufacturing Facilities in Japan Independent Practitioner's Assurance
Komatsu is aware of the harmful environmental impacts that certain materials possess, and has made continuous efforts from an early stage to reduce the use of a number of such substances. These included asbestos, lead, and other such items. In FY 1999, we created our own list of banned and limited-use substances (Refer to “Substances of Environmental Concern Banned or to Be Reduced for Use in Products”), which was based in part on Japanese legislation (Japanese Law Concerning the Examination and Regulation of Manufacture of Chemical Substances Control) that banned a number of chemical materials as well as regulatory measures in other countries.
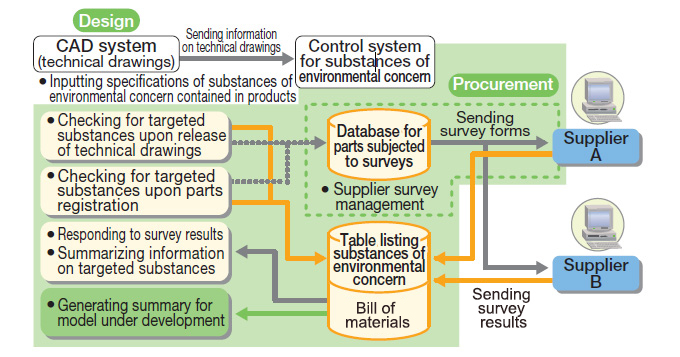
We have also implemented more stringent measures in the control of substances that raise environmental concerns. In compliance with REACH*1 and SCIP*2, we began revisions of our FY 1999 listing of banned and limited-use substances. We have also collaborated with suppliers to create a regulatory system that strengthens control of potentially harmful materials being used for production. We have rolled this system out in Japan and Europe, with plans to continue implementation in other areas of operation.
Through the use of this system, we identify SVHC (substances of very high concern) in not only vehicles for export to the EU or produced at local EU companies, but also in vehicles currently in production and in newly developed vehicles. Furthermore, we also regularly check for new SVHCs to be added to the list.
As of May 2025, there are 247 SVHCs registered, with the list being revised every six months. We expect this number to increase to about 1,500 in the future. We have also devised a workflow to monitor control of these substances.
| Rank | Number | Chemical Substance |
|---|---|---|
| Banned |
21 |
|
| To be reduced (Subject to limited use) |
15 |
|
| Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) under EU REACH Regulations |
(247)*5 |
Komatsu controls the use of the following substances, which might be used in Komatsu products.
|
We are reducing and ending our use of substances of environmental concern.
To reduce the NOx (nitrogen oxide) and PM (particulate matter) contained in the exhaust gases of diesel engines, which are used in construction equipment and other machinery, new emission control regulations have been established, and we have been developing products that emit cleaner exhaust gasses. About 73% of the construction machinery manufactured in FY2024 complies with regulations equal to or more stringent than U.S. Tier 3 and EU Stage IIIA regulations. As a result, the average NOx and PM emitted by the construction equipment products produced by Komatsu are shown below:
Average emission value of NOx and PMIndependent Practitioner's Assurance
| FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOx(g/kWh) | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.9 |
| PM(g/kWh) | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
Due to climate change, population growth and other phenomena brought by global warming, risks of river flooding, droughts, water shortages and other water-related problems have surfaced all over the world and are becoming more serious every year.
The Komatsu Group believes that everyone has the right to access to safe and sanitary water, and we respect it as one of the most important rights. We also fully understands that we depend on that water and our business operations are influenced by and exert influence on the quantity and quality of that water.
Therefore, we engage in production activities that minimize environmental impact, provide good products and services and take appropriate actions to mitigate water-related risks in an effort to conserve local water resources and ensure that the water stays safe. It is our goal to promote these activities at All Komatsu and lead to the conservation of the global environment.
Through these initiatives, we contribute to the SDGs, a set of common goals for the world.
Based on the Komatsu Earth Environment Charter, the Komatsu Group has promoted the reduction of water usage, recycling, and activities focused on water quality protection. In 2023, we conducted a "Water Risk Survey" at 58 key business sites, both domestic and international, regardless of production status. This survey included: (1) the identification of general and objective water risks using the WRI Aqueduct, and (2) a subjective awareness survey of water risks deemed important by Komatsu. By combining these two approaches, we achieved a more comprehensive "Water Risk Survey."
The results of this "Water Risk Survey" revealed that some areas within the Komatsu Group face significant risks, such as water scarcity (water stress) and disaster risks from river flooding. Moving forward, we will continue to conduct regular "Water Risk Surveys" to update and address water-related issues within the Komatsu Group.
Using WRI Aqueduct, we surveyed the water stress risks at 30 main domestic and international production bases of the Komatsu Group, focusing on the use of water resources necessary for production activities, including clean water (tap water/city water), industrial water (clean water for industrial use), and well water.
As of 2023, the business locations rated as having high or middle-to-high water stress risks accounted for approximately 6% of our total water usage. While about 68% of the water used by Komatsu overall is well water, we found that all the water used in the locations with high water stress risks is clean water. This underscores the importance of reducing water usage and increasing water recycling to secure water resources in these areas.
We will effectively use these survey results for activities we have conventionally engaged in, such as the promotion of water usage (input volume) reduction and recycling, adaptation to physical risks of heavy rain and flood, aiming to reduce the water-related risks the Komatsu Group is exposed to. In addition, when planning the construction of a new business base or the transfer of a base, we will survey water stress in that area to identify the risk level.
We have initiated the construction of multiple safety measures against the risks imposed by heavy rain. These include the building of three reservoirs (capable of holding up to an hour's worth of 100mm/h rainfall), installation of heavy rainfall water pipes, the construction of underground reservoirs, and the widening of rainwater drainage ways. In addition to this, we have installed water block walls and stop bars to prevent water from flowing outside of the premises.
Current Status of Reservoirs:
KIPL: Flooding from rivers may enter the parts warehouse and remanufacturing store during heavy rainfall. The following measures have been taken to prevent the entry of river flood water:
KRA: This area receives heavy rainfall and is located in a canyon, so large amounts of water may enter the site. The following measures have been taken to prevent the entry of water:
Our water-related risk survey was conducted at the operations of one of our main supply chain companies (Midori-kai), and Midori-kai has made collaborative efforts in our water-related risk reduction activities since FY2017.
Komatsu has been conducting planned compliance and risk audits (CR audits) since FY2007 to prevent risks at overseas subsidiaries.
In FY2024, we conducted audits in Indonesia. The audits were carried out with the support of environmental managers at mother plants in Japan, after verifying the self-check sheets prepared by the local subsidiaries. The results showed that none of the companies had any major problems that could lead to environmental risks, and they were all actively engaged in activities to reduce their environmental impact.
We will continue to conduct follow-up audits and expand environmental audits to local subsidiaries in other regions.
| Year | Area | Year | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | China | 2016 |
India and Indonesia |
| 2008 | — | 2017 | Russia and China |
| 2009 | Thailand and Indonesia | 2018 | Indonesia and Brazil |
| 2010 | India | 2019 | China and the United States |
| 2011 | Brazil | 2020 | Europe |
| 2012 | Russia and Czech Republic | 2021 | China and Europe |
| 2013 | United State | 2022 | Southeast Asia and the United States |
| 2014 | United States and Brazil | 2023 | Europe, China, and North America |
| 2015 | Thailand | 2024 | Indonesia |
At Komatsu, we hold a global environment meeting in Japan (at the Komatsu Way Global Institute) once every three years. In the remaining two years, we organize regional environment meetings in each area. These meetings provide opportunities to exchange information and discuss region-specific challenges, with the aim of enhancing compliance and environmental impact reduction efforts at each site.
In FY2024, we held the global environment meeting for the first time in six years, as it had been postponed several times due to the COVID-19 pandemic. A total of 55 environmental representatives from Komatsu Group companies and sites in Japan and overseas participated. The meeting served as a forum for sharing the latest updates on environmental initiatives at each company and global environmental trends, as well as discussing the environmental actions we should pursue going forward. During the meeting, participants also visited key sites including the Awazu Plant and the Komatsu Toyama sales office.
Through initiatives like this, we aim to further revitalize environmental activities across the Komatsu Group.